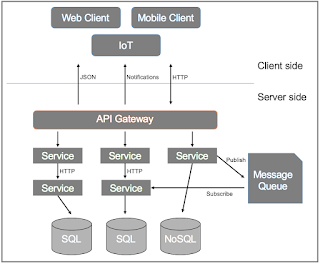
- Microservices operate independently, allowing for flexible and autonomous deployment.
- Examples of microservices include User Service, Order Service, and Inventory Service, among others.
Database Per Microservice:
- Each microservice is paired with its own dedicated database to promote data isolation, scalability, and autonomy.
- For instance, the User Service interacts with its User Database, while the Order Service manages its Order Database.
Interactions Between Microservices and Databases:
Read Operations:
- Microservices access data from their designated databases to perform operations effectively.
- When requiring user information, the User Service directly queries its User Database.
Write Operations:
- Microservices update data within their respective databases seamlessly.
- For instance, when a new user registers, the User Service efficiently inserts the user details into its User Database.
Database Connection Pooling:
- Maintaining connection pools ensures efficient management of database connections.
- Each microservice maintains a connection pool to minimize connection overhead and enhance performance.
Service-to-Service Communication:
- Microservices communicate using protocols such as HTTP/HTTPS for RESTful APIs and Message Queues for publish-subscribe.
- For example, the Order Service requests user information from the User Service API via an HTTP request, facilitating seamless data exchange.








